Perinatal Hepatitis B - HAN
Jump To:
Overview
Prevention of perinatal hepatitis B infection requires prenatal identification and early reporting of HBV-infected mothers [hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) positive] during each pregnancy.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommend:
- Universal testing of pregnant women for HBsAg,
- Testing HBsAg-positive pregnant women for HBV DNA.
- Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) within 12 hours of birth with HBIG and the first dose of HepB vaccine for infants born to HBV-infected mothers,
- Universal HepB vaccination within 24 hours of birth for medically stable infants weighing ≥2,000 grams regardless of the mother’s HBsAg status.
- Completion of a valid three or four dose vaccine series in all infants, and
- Post-vaccination serologic testing (PVST) for HBsAg and anti-HBs at 9-12 months for infants born to HBV-infected mothers or infants born in regions of high and intermediate HBV endemicity.
ROLE OF CDPH:
- Review of all HBsAg positive laboratory results in women of child-bearing age and determine pregnancy status.
- Enroll HBsAg positive women and their infants in the PHBPP.
- Collaborate with healthcare providers, delivery hospitals, laboratories, and families in Chicago to ensure identification of HBsAg positive mothers, treatment of infants at birth, timely completion of hepatitis B vaccination, timely and appropriate post-vaccination serologic testing, identification and referral of household contact, and appropriate education of patients.
- Complete documentation of case management of mothers in INEDSS and mothers and infants in CDPH data base(s).
- Provide follow-up education as needed to the healthcare partners on reporting and appropriate immunoprophylaxis, vaccination and testing.
- Provide standardized culturally appropriate health education materials to reinforce the importance of preventing perinatal hepatitis transmission.
ROLE OF CLINICIANS:
- Notify CDPH for all HBV+ mothers.
- Select a test designated as “prenatal” or on a prenatal/obstetric panel when ordering an HBsAg screening test for a pregnant woman to help ensure confirmatory testing is performed on all positive HBsAg screens.
- Inform selected laboratory of a woman’s pregnancy status to ensure confirmatory testing is performed on all positive HBsAg screens.
- Include any and all ICD 10 diagnosis codes indicating current or recent pregnancy when ordering HBsAg tests
Screening of Pregnant Women
- Initial screening: All pregnant persons shall be tested for HBsAg (hepatitis B surface antigen) during an early prenatal visit, or when they present to a hospital for delivery if prenatal serologic results are not available.
- This testing is required by the IL Public Health Code Section 690.451 c) 1).
- Re-test pregnant persons who are at high risk for HBV infection (recent history of sexually transmitted disease, injection drug use, or other possible risks of HBV infection) upon admission to the hospital or birthing facility for delivery.
- Persons known to have a chronic HBV infection should be tested again at each pregnancy regardless.
- Interpretation of Hepatitis B Serologic Test Results (CDC)
- Guidance on the interpretation of Hepatitis B serologic test results.
- Discrepant Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) lab results during pregnancy: recommended next steps (CDC)
- A guide for determining management of infants born to a pregnant person with an initial confirmed HBsAg positive result followed by a negative result during the same pregnancy
- Screening and Referral Algorithm for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Infection Among Pregnant Women (CDC)
- Algorithm detailing appropriate follow-up for pregnant women with positive HBsAg results.
Hepatitis B Reporting
| Lab Reporting | Laboratories are required to report positive results indicating HBV infection to local health departments/Chicago Department of Public Health (CDPH). Lab reports can be submitted through: |
| Provider Reporting | Providers should report all HBV+ pregnant persons to CDPH for case management via I-NEDSS (preferred), via the Online Case Reporting Form, or by phone at 312-743-9000 |
| APORS (Adverse Pregnancy Outcome Reporting System | Hospitals are required to report births to HBV+ Persons to APORS with 7 days of discharge |
Hepatitis B PEP and Vaccination for Exposed Infants
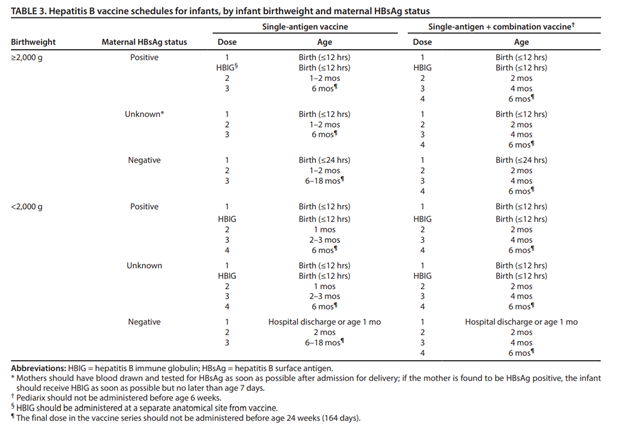
A detailed hepatitis B vaccination schedule, including guidance for the single-antigen vaccine, the combination vaccine, and for infants <2,000 grams can be found in the table below and the catch-up schedule here.
- Procedures to Prevent Perinatal Hepatitis B Virus Transmission at Delivery (CDC)
- Algorithms illustrating delivery hospital procedures to prevent perinatal HBV transmission (e.g. PEP, vaccine, and screening) when maternal HBsAg test results are available and unavailable.
- Hepatitis B Immunization Materials for Patients and Staff (Immunization Action Coalition)
- Education materials and resources for the Hepatitis B vaccine for both patients and healthcare providers. Includes handouts, FAQs, VISs in multiple languages, and standing order template.
- Childhood and Adolescent Vaccination Schedule (CDC)
- Routine and catch-up vaccination schedules for children 18 years and younger.
Serology Testing for Exposed Infants
| Anti-HBs Result | HBsAG result | Follow-up Needed? |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | None. Infant is protected |
| Negative | Negative | No response. Infant is susceptible to infection. Administer a single dose of HepB vaccine and repeat postvaccination serologic testing 1–2 months later. Infants whose anti-HBs remains <10 mIU/mL following single dose revaccination should receive two additional doses of HepB vaccine to complete the second series, followed by postvaccination serologic testing 1–2 months after the final dose. |
| Negative | Positive | Infant is infected with hepatitis B. Consult with liver specialist. |
Perinatal HBV Case Definition
PROBABLE CASE:
- If a child born in the US and positive for HBsAg at ≥ 1 month of age and ≤ 24 months of age OR
- If a child is positive for HBsAg or HBV DNA ≥9 months of age and ≤ 24 months of age, but whose mother’s hepatitis B status is unknown (i.e. epidemiologic linkage not present).
- If a child born in the US to a HBV-infected mother and positive for HBsAg at ≥ 1 month of age and ≤ 24 months of age OR
- If a child is positive for HBeAg or HBV DNA ≥9 months of age and ≤ 24 months of age.
Hepatitis B Testing and Support
230 W. Cermak 2nd floor
Chicago, IL 60616
F: (312) 225-8659
Maggie Li, maggieli@maha-us.org;
Arista Wang, maristawang@maha-us.org
www.maha-us.org
Provider Resources
- CDC: General Hepatitis B Information
- Information and resources for providers and the public on hepatitis B vaccination, testing, transmission, and prevention.
- CDC: Perinatal Transmission
- Information on perinatal transmission of HBV and the national strategy to eliminate perinatal hepatitis B. Includes information on testing providers, provider decision aids, and patient education materials.
- Management of Infants Born to Women with Hepatitis B Virus Infection for Pediatricians (CDC)
- Provider tip sheet describing management of infants born to HBV-infected persons, guidance on interpreting post vaccination serologic testing results, and frequently asked questions.
- Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: Recommendation of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP)
- ACIP recommendations on HBV prevention, including: screening of pregnant women and management of infants born to persons who are HBsAg-positive or have unknown HBsAg status.
- Hepatitis B: What Hospitals Need to Do to Protect Newborns (Immunization Action Coallition)
- Guidebook for hospitals on screening, post-exposure prophylaxis, and universal birth dose implementation, including example policies and standing order templates.
- Update on Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 Hepatitis B Guidance
- Guidance on prevention, screening, and care of patients with chronic hepatitis B from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Patient Education Materials
- Hepatitis B and a Healthy Baby (CDC)
- Plain language educational slide set for mothers with Hepatitis B emphasizing the importance of vaccinating their child. Available in English, Chinese, Hmong, Korean, Vietnamese, and Tagalog/Taglish.
- Hepatitis B and Your Healthy Baby (CDC)
- Educational slide set for mothers with Hepatitis B on HBV basics and Hepatitis B vaccination.
- Perinatal Transmission Patient Fact Sheets (CDC)
- Handouts and infographics on Heptatitis B and Hepatitis B vaccine for parents with or without HBV infection.
- Hepatitis B Vaccine Information Statement (CDC)
- Mandatory Vaccine Information Statement (VIS) to be distributed at the time of vaccination. Official translations into additional languages can be found here.
To report suspect or confirmed cases:
Lab Reporting:
Laboratories are required to report positive results indicating HBV infection to local health departments/Chicago Department of Public Health (CDPH). Lab reports can be submitted through:
- Electronic laboratory report to I-NEDSS (Preferred)
- Faxing reports for hospitals/outpatient labs to: 312-746-4683.
Provider Reporting:
Providers should report all pregnancies with evidence of acute or chronic hepatitis B infection to CDPH via:
- I-NEDSS (preferred) OR
- Use the Online Case Reporting Form OR
- Contact the CDPH Disease Reporting Hotline at 312-743-9000, option 2.
APORS (Adverse Pregnancy Outcome Reporting System): Hospitals are required to report births to HBV+ persons via APORS with 7 days of discharge
Questions:
Contact Divina Vargas, Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program CoordinatorEmail: Divina.Vargas@cityofchicago.org
P: (312) 747-9609
Hepatitis-B Screening and Support Services for Families at High Rish
MIDWEST ASIAN HEALTH ASSOCIATION
230 W. Cermak 2nd floor
Chicago, IL 60616
F: (312) 225-8659
Maggie Li, maggieli@maha-us.org;
Arista Wang, maristawang@maha-us.org
www.maha-us.org
